When inspecting and accessing tight spaces, having the right video borescope is a must. But with so many different types and sizes of video borescopes available, how do you know which one is best for your application? This guide will help you figure out which features are important when choosing a video borescope, so you can make an informed decision about what's best for your needs.
This Part 1 of a 2-part video borescope blog series.
Video Borescope Choices
When choosing a video borescope for your application, there are multiple considerations that must be made to select the right tool for the job:
- Inner Diameter (part opening and core passage being inspected)
- Outer Diameter (video borescope)
- Field of view
- Direction of view
- Articulation
- Illumination (not covered in this article)
Inner Diameter of Part
Simply put, the inner diameter, or ID, refers to the width of the part’s bore or passage being inspected, usually measured in units of inches or millimeters. Knowing your part/application ID dimensions is critical. This is the first consideration in choosing a video borescope.
Outer Diameter of Scope
The outer diameter, or OD, of the video borescope is the width of the scope tip. Usually measured in millimeters, this criterion is also critical in choosing the proper scope for your application. Certain ODs of scopes work well with certain part/application ID’s.
Field of View
Field of view (FOV) is the visible area a video borescope can see at once. This is measured in horizontal degrees (H°), or sometimes horizontal by vertical degrees (H° x V°).
As FOV increases, the total area of the image increases. Similarly, as FOV decreases, the total area of the image decreases.
While most video borescopes have a fixed-focus lens (no “zoom” feature), the FOV can help indicate magnification of an image. As FOV increases, objects appear smaller in size, and as FOV decreases, objects appear larger in size. This is best illustrated in the image below:

Direction of View

Direction of view (DOV) refers to orientation of the camera sensor on the distal tip of the video scope. Direct view looks forward (or 0°) from the scope tip, side view looks to the side (or 90°), and dual view can look in either direction. 0° DOV scopes are useful in locating defects inside parts as you maneuver into a part, and 90° DOV scopes are useful for closer side-wall inspection and documentation. Dual view (both 0° and 90°) provides both options for more thorough inspections.
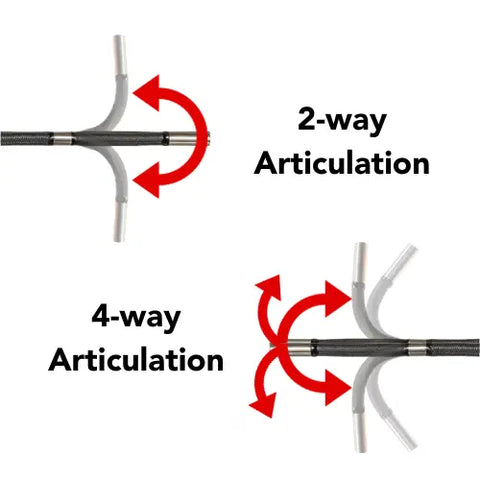
Articulation
Articulation refers to whether a video borescope can move the distal tip of the scope from a simple control mechanism. 2-way articulation means a scope can sweep back and forth on a single plane. 4-way articulation means a scope can sweep back and forth on 2 separate planes allowing for more inspection coverage without scope rotation. The below illustrates the difference between 2 and 4-way articulation.
Choosing a Video Borescope
From InterTest’s collective experience in serving customers for over 40 years, the following is a quick reference guide showing examples of video borescope OD’s used to inspect the listed part ID’s.
|
Part/Application ID (in) |
Recommended Video Borescope |
|
< ¼” ID parts |
Cannon Medical SV-2000 0.89, 1.05 & 1.6 mm OD, Direct View, No Articulation |
|
Yateks P+ Series 1.1 mm OD, Direct View, No Articulation Yateks P+ Series 1.7 mm OD, Direct View, 2-way Articulation |
|
|
Zibra Milliscope HDV 1.2 & 1.6 mm OD, Direct View, No Articulation |
|
|
¼” to ½” ID parts |
Yateks P+ Series 2.2 mm OD Direct View, 2-way Articulation |
|
Yateks P+ Series 2.2 mm OD Side View, 4-way Articulation |
|
|
Yateks P+ Series 2.8 mm OD, 4-way Articulation:
|
|
|
Zibra Milliscope HDX 2.5 mm OD, Direct or Side View, 2-way Articulation |
|
|
Zibra Milliscope HDV 2.6 mm OD, Direct or Side View, No Articulation |
|
|
½” to 1” ID parts |
Yateks P+ Series 3.9 mm OD, 4-way Articulation |
|
1” to 2” ID parts |
Yateks P+ Series 6.0 mm OD, 4-way Articulation |
|
~ 3” to 5” ID parts |
Yateks P+ Series 6.0 mm OD, 4-way Articulation |
|
Yateks P+ Series 8.4 mm OD, Dual View, 4-way Aritculation |
|
| Wohler VIS 700 HD |
This quick reference guide has FOV, DOV and illumination considerations, but every application will vary. This information is generalized and educational, so let InterTest, Inc. help you choose the best video borescope for you needs.
Contact us immediately and one of our seasoned professionals will ensure you choose the best video borescope for your remote vision inspection application.

